Taxation is the imposition of compulsory levies on individuals or entities by governments in almost every country of the world. Taxation is used primarily to raise revenue for government expenditures, though it can serve other purposes as well.
In modern economies, taxes are the most important source of governmental revenue. However, taxation is not a government’s only source of revenue. Taxes differ from other sources of revenue in that they are compulsory levies and are unrequited (except payroll taxes)—i.e., they are generally not paid in exchange for some specific thing.
Types of Taxes
There are Two types of Taxes in Nepal which are as follows:
- Direct Tax
- Indirect Tax
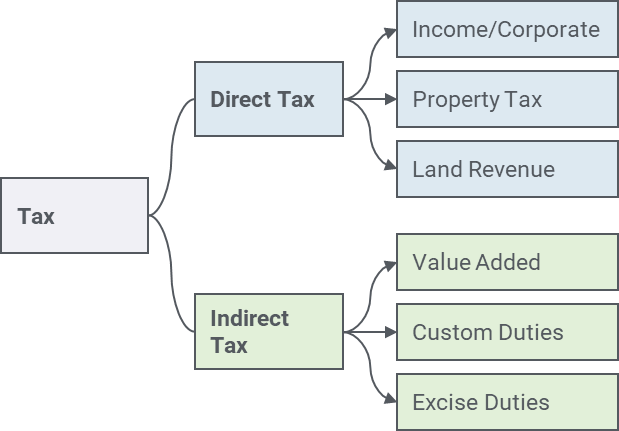
1. Direct Tax
Direct tax is paid by an individual or organization to the entity that levied the tax. Direct taxes cannot be shifted to another party and remain taxpayer responsibility to pay. Direct taxes are one type of taxes an individual pays that are paid straight or directly to the government. Direct taxes are computed based on the ability of the taxpayer to pay, which means that the higher their capability of paying is, the higher their taxes are.
Direct taxes include:
- Income Taxes/Corporate Taxes
- Property Taxes
- Land Revenue
1.1 Income Tax and Corporate Tax
Income tax is governed by Income Tax Act 2058. Income tax is a tax charged on the taxable income. Taxable income is derived by deducting the allowed expenditures from the revenues and the gains.
So, the formula may be framed like this:
Revenue + Gains – Allowable Expenses = Taxable Income
Income Tax Rates in Nepal 2079/80:
| In case of Individual | In Case of Couple | Rate Of Tax |
| First Rs. 5,00,000 | First Rs. 6,00,000 | 1% |
| Next Rs. 2,00,000 | Next Rs. 2,00,000 | 10% |
| Next Rs. 1,00,000 | Next Rs. 1,00,000 | 20% |
| Next Rs. 7,00,000 | Next Rs. 600,000 | 30% |
| Above 1500,000 | Above 1500,000 | 36% |
Corporate tax, also called company tax or corporation tax, is a direct tax levied on a company’s income or capital by the government.
Corporate Tax Rates in Nepal 2079/80:
| SN | Particulars | Normal Rate (%) | Rebate (%) | Applicable Rate (%) |
| 1 | Normal Business | 25 | – | 25 |
| 2 | Special Industry Under Section 11 for the whole year | 25 | 20 | 20 |
| 3 | Entities constructing and operating ropeway, cable car or sky bridge | 25 | 40 | 15 |
| 4 | Entities constructing and operating roads, bridges, tunnel, railway, and airports | 25 | 50 | 12.5 |
| 5 | Entities operating trolley bus or trams | 25 | 40 | 15 |
| 6 | Entities with export income from source in Nepal | 25 | 20 | 20 |
| 7 | Entities involved in construction or operation of public infrastructure and to be transferred to GoN or involved in construction of hydropower house and its generation and transmission. | 25 | 20 | 20 |
| 8 | Banks and financial institutions (Commercial Banks, Development Banks and Finance Companies) | 30 | – | 30 |
| 9 | Entity carrying General insurance business (Non-life Insurance) | 30 | – | 30 |
| 10 | Entity engaged in petroleum business under Nepal Petroleum Act, 2040 | 30 | – | 30 |
| 11 | Entity engaged in business of cigarette, tobacco, cigar, chewing tobacco, pan masala, alcohol and beer | 30 | – | 30 |
| 12 | Entity engaged in Telecommunication and Internet service | 30 | – | 30 |
| 13 | Entity engaged in Money transfer | 30 | – | 30 |
| 14 | Entity engaged in Capital market business, Securities business, Merchant banking, Commodity future market, Securities and Commodity broker | 30 | – | 30 |
1.2 Property Tax
Property taxes are levied as per Section 55 of the Local Government Operation Act 2074 (2017) and is calculated on the real property (land and building) on the basis of municipal valuation of the land and the cost of the building (plinth area) at a fixed rate for the type of structure. The type of the land, building, market value of the land and depreciable cost of the building and the use for commercial or residential purpose is considered when determining the value of the property.
For the purpose of property tax, the land means the building and the area of land on which the building is constructed, or 5,476 sq. ft. land, whichever is lower.
1.3. Land Revenue
Land revenue is levied by the Municipality on the land on which property tax has not already been levied as per section 55 of the Local Government Operation Act 2074 (2017).
2. Indirect Tax
Indirect taxes are those taxes that can be shifted from one individual to another. It is not levied directly on the income of the taxpayer, but is levied on the expenses incurred by them. Some examples of indirect taxes include
- Value Added Tax
- Excise duty
- Custom Duty etc.
2.1 Value Added Tax
Value Added Tax is governed by VAT Act 2052. Value Added Tax (VAT) is indirect tax that is based on goods and services. This tax is levied on the sale, exchange, transfer, import etc. of all goods and services apart from those specified by the law as tax-exempt. This means that this tax encompasses all types of goods and services produced in or imported into the country apart from those listed as tax-exempt by the law. VAT is considered as an improvised form of sales tax. This tax is imposed on different levels of value addition in the production and distribution process of goods and services.
In short, the difference between the purchase price and the sales price of any firm is the value added. In practice, the tax-payer does not have to calculate his value addition for the purpose of VAT. But s/he has to collect VAT on the sales price at the rate specified by the VAT Act and after deducting the VAT paid on purchases from the amount thus collected and s/he has to pay the balance amount as VAT. Under VAT each registered manufacturer and distributor must collect tax on the sales of their goods and services.
Rate
VAT is levied at a flat rate of 13 percent, which is applied to the invoice value. Certain specified goods are outside the scope or exempt from VAT. Exports of both goods and services are taxed at zero percent.
Threshold
Threshold for compulsory registration under VAT Act is a turnover exceeding NR 5 million over the last 12 months in case of goods, and NRs 2 million for services or both services and goods. Exemptions apply inter alia, to salaried employment, banking and financial services, education and health services, agriculture produce and certain non-profit making activities.
Certain businesses require compulsory registration for VAT purposes. These include: Production and transaction of bricks, Alcohol, Wine, Health Club, Discotheque, Massage Therapy, Motor Parts, Electronic Software, Custom Agent, Toys Business, Trekking, Rafting, Ultra-light Flight, Paragliding, Tourist Vehicle, Crusher, Sand Mine, Slate or Stone. Other business that requires compulsory registration if conducted in metropolitan city, sub metropolitan city and municipality: Hardware, Sanitary, Furniture, Fixture, Furnishing, Automobiles, Electronics, Marble, Educational Consultancy, Accounting and Audit related services, Catering Service, Party Palace, Parking Service, Dry Cleaners using Machinery.
Restaurant along with Bar, Ice cream Industry, Color Lab, Boutique, Uniform suppliers for Educational Institutions, Health Service Organizations or similar institutions.
Reverse Charge of VAT
Where a person Nepal, whether registered or not, avails services from a non-resident, is required to collect VAT on value of services availed on reverse charge system and deposit the same with the tax authorities. VAT collected shall be permitted for input VAT credit.
Furthermore, according to Section 8(3) of VAT Act, any person whether registered or not in Nepal if engaged in construction of commercial buildings, apartments, shopping malls or similar other structure as specified by IRD having value more than NRS 5 million, then tax has to be deposited on the construction cost as if it has been constructed from registered person. Construction should be for business purpose. Business purpose means for sale or for use in income generation.
Tax Credit
To avoid double taxation, a credit is given for VAT paid on goods and services used for the purpose of making any taxable supply (Input VAT). A credit is also given for VAT paid in respect of certain exempt supplies, e.g., exports. The principal mechanism for collecting the tax requires the taxable supplier to charge VAT on the goods or services supplied (Output VAT) to take credit for VAT paid on business expenditure (Input VAT), and to pay the net tax over to the authorities.
Tax Refund
The excess credit after setoff is available for refund if the amount remains unsettled for 4 months. Also, special immediate refund facility is available for industries that export more than 40% of total sales. VAT paid in Nepal by a diplomat of a foreign country to Nepal (as recognized by GON, Ministry of Foreign Affairs), if the foreign country grants the same on a reciprocal basis, are available for set off under diplomatic refund facility.
Refund of VAT paid on the purchase of goods or services in Nepal by United Nations Organization, its member organization and specialized agencies while carrying out the activities as per their objectives if application for refund is received within 3 years of such procurement.
VAT paid on the purchase of raw materials, auxiliary raw materials and packing material of medicines from domestic industry for manufacturing by medicine industry shall be refunded on a four-monthly basis upon application to the IRD. If application for VAT refund is received by the tax officer, the refund shall be made within 60 days from the date of application.
VAT withheld and deposited on behalf of the contractors by government entity (fully or partially owned), public institution, or association for the purchase of goods and services under contract shall be adjusted against the VAT payable of the contractor. The VAT amount so deposited by the government entity, if there remains an excess after offsetting for a continuous period of 4 months, the contractor at his will shall submit an application for refund to the tax officer.
Requirements
VAT registrants are required to:
- Submit VAT return and pay tax within the 25th day of the following month
- Provide their customers with a tax invoice
- Maintain purchase book, sales book, VAT account
- Keep their VAT records for a period of 6 years
- Inform the IRO of changes to the business including new address, telephone number or a reorganization of a partnership within 15 days.
2.1. Excise Duties
Excise duties are payable on the manufacture of movable goods and also on import of certain goods.
Excise duties are governed and regulated by the Excise Act 2058 (2002) and Excise Regulation 2059 (2003). As provisioned in the law, the excise commodities subject to physical control system are closely controlled and supervised by the GoN from their production to selling stage.
License Required
No one is allowed to manufacture, import, sell and store excisable goods without obtaining a license. Likewise, the law prohibits import of excisable services without having a license. Person, firm or institutions who need such a license may submit a prescribed application form before an excise officer at the concerned IROs.
Rate
The rate of excise duty ranges from 0% to 100%. Exports are exempt from excise duty.
Others
- Abatement of 100% on excise duty on purchase of bus having seat capacity of 30 or more for community schools. The benefit is available for one bus per community school. Vehicles imported under such a facility shall not be sold, transferred and changed ownership within 10 years.
- In case of filtered cigarettes, the excise rate has been increased by approximately 20% on the basis of length of filter.
- Increment in excise rates of paint from 5% to 7%.
- Excise duty has been increased from 60% on 4 wheelers on the basis of cylinder capacity starting from 1000 to the extent of 65%, 70%, 80%, 85%, 90% and 100%.
- Excise duty has been increased from 40% on motorcycle on the basis of cylinder capacity starting from150cc to the extent of 50%, 60%, 80% and 100%.
- On the basis of concentration of alcohol in wine, the excise rate has been increased ranging from 19.64% to 20%.
- Excise duty has been introduced on energy drinks at the rate of NRS 30/litre.
- Introduction of 5% excise rate in case of perfumed water or water for sanitization, cosmetics, hygiene and make-up items.
- NRS 1,650 per metric ton excise duty in case of steel pipes, bridges, tower and other steel structures.
- 5% excise duty for refrigerator, freezer, vacuum cleaners, juice extractors and its parts, puzzles, toys, video games, billiard and special tables for casino.
- 5% excise duty in case of chocolates containing cocoa or not and 10% in case of other chocolate layered or not layered with sugar.
2.3 Customs Duties
Customs duties are calculated on transaction value which includes cost, insurance & freight up to Nepal border on the import of goods. In case there is under invoicing, the customs official can revalue the goods based on current market value and collect customs duties on such amount or purchase the goods at the under invoiced value as it so considers.
Customs Service Fee (CSF) of NRS 500 per declaration form will be charged at the time of import of goods into Nepal. Similarly, CSF of NRS 100 per declaration form will be charged at the time of export of goods from Nepal.
Rate
Customs duties range from 0% to 80% on the transaction value depending on the products. Most raw materials fall within the 0% to 10% duty band, whereas finished goods and consumer items fall within the 5% to 30% duty band. Duties at the rate of 80% are levied on only a few items (i.e., motorcar, arms and ammunition and pipe tobacco). In the case of export there are generally no duties except for certain products, like those originating from forests, certain agricultural products that are in short supply in Nepal or industrial raw materials and minerals.
Exim Code
Exim code is required to be obtained from the Department of Customs by all importer of goods. The timing for registration of an importer on EXIM code shall be 2-3 days provided that all the documentation is well provided. Exim Code is renewable every year.
Others
- Goods of Indian origin being imported from India can be imported on concession of 5% on customs duties from 5% up to 30%. But a 3% concession can be obtained on goods for which customs duties are above 30% (where custom duty is levied on value).
- Resident of Nepal returning from a foreign country can bring gold up to 100 gm after payment of NRS9,500 per 10 gm up to 50 gm and NRS 10,500 per 10 gm for next 50 gm. Gold in excess of 100 gm shall be seized by the customs office.
- 5% customs duties shall be levied on urine bag imported on the recommendation of Ministry of Health and Population.
- Abatement of 75% on customs duties on purchase of bus having seat capacity of 30 or more for community schools. The benefit is available for one bus per community school.
- 50% rebate on customs duty for fertilized eggs under tariff Sub Heading 0407.11.00 and 0407.19.00 imported by poultry industry for production of chicks.
- 50% custom duty rebate on vehicles having only electric stroke engines under heading 87.02, 87.03, 87.04
- 50% custom duty rebate on machinery for making face mask imported by industry producing face mask under heading 8449.00.10
Miscellaneous
Import of old and used goods are prohibited except for the following:
- Equipment and machineries under heading 84 up to 5 years old from the date of manufacture required for the operation of industry. Printing Industry can import old printing machine up to 10 years.
- Metal scrap.
- Parts and accessories of repaired and overhauled Air Planes and Helicopters approved by Civil Aviation Authority of Nepal or other similar authorized authorities.
- Old personal belongings imported as per provisions of baggage rules.
- Old machineries imported with condition for re-export.