1. Human Resources
Human Resources is used to describe both the people who work for a company or organization and the department responsible for managing resources related to employees.
In Nepal, the Human Resources are governed by the Labor Act,2074 and Labor Rules,2075. This Labor Law applies to companies, Private Firms, Partnership firms, cooperatives and Industries These laws have aimed to protect employees rights and set forth employees obligation with respect to employment.
The-Labor-Act-2017-2074
The basic employment standards to be assembled by a start up companies as per the Labor Act 2074, Section-2 are:
- Written employment agreement or contract while hiring any employee.
- Guarantee minimum standard remuneration, occupation, health and safety measures in the workplace.
- Provide entitlements such as festival allowances, insurances, bonus etc.
- Make arrangements for Provident fund, Gratuity, Leave, Social Service Accounts.
2. Types of Employees
Under Section 10 of the Labor Act,2074 it has mentioned the types of Employee. The company may hire employees on the basis of the following classification provided by the Labor Act,2074 as per the company requirements:
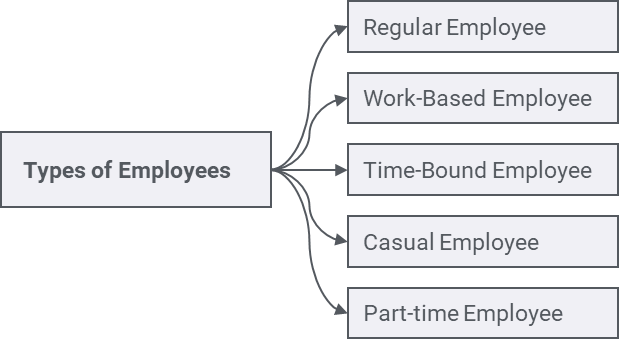
- Regular Employee
All employees who work for a regular nature of work under a contract without any end date are considered as regular employees - Work Based employee
Employees who are hired for carrying out a specific work or rendering specific services are considered as work-based employees. - Time Bound Employees
Employees hired for providing services for a definite period of time under a contract with an end-date are considered as Time Bound employees. - Casual Employees
Employees hired for providing service for seven days or less in a month are considered as Casual employees. - Part-time Employees
Employees hired to work for 35 hours or less in a week are considered as Part-time employees. The remuneration of Part-time employees is based on the hours worked. (Section 19-21).
3. Employment Agreement/Contract
Contract is the agreement between two or more than two parties with some considerations. In the employment contract there are two parties i.e. employer and the employee. If the company is interested in hiring someone then it must create a standard employment contract covering the type of employment and the time period. The company needs to provide an employment agreement before engaging him/her in the company.
The employment agreement needs to include the following information:
- Name and address of the employee and employer
- Nature of the employment
- Employee’s Job Title or Position
- Monthly salary
- Job description
- Work hours and Days
- Entitlements
- Any other conditions as per service and work of the employee
4. Remuneration(Section 34)
Each worker is entitled to receive the remuneration and benefits from the date on which he/she starts the work. The remuneration and benefits should be specified in the employment contract.
The remuneration of the employees should not be below the minimum wage prescribed by the Ministry of Labor, Employment and Social Security. The current minimum wage of employees as per the Gazette Notice dated May 03,2021 is mentioned below:
| S.N | Minimum Remuneration | Basic Remuneration | Dearness Allowances | Total (Rs.) |
| 1. | Monthly | 9,385/- | 5,615/- | 15,000/- |
| 2. | Daily | 361/- | 216/- | 577/- |
| 3. | Hourly | 48/- | 29/- | 77/- |
salary-2078-01-20
Source: Notice published on Nepal Gazette on 2078/01/20.
5. Taxation on Salary
According to Inland Revenue Department, following are the income tax rates for unmarried individuals in Nepal for the Fiscal Year 2079/80:
| Annual Income | Income Tax Rate |
| Up to Rs. 5,00,000 | 1% |
| Rs. 5,00,001 to Rs. 7,00,000 | 10% |
| Rs. 7,00,001 to Rs. 10,00,000 | 20% |
| Rs. 10,00,001 to Rs.20,00,000 | 30% |
| Above Rs. 20,00,000 | 36% |
The table below presents the income tax rates in Nepal for married couple for the Fiscal Year 2079/80:
| Annual Income | Income Tax Rate |
| Up to Rs. 6,00,000 | 1% |
| Rs. 6,00,001 to Rs. 8,00,000 | 10% |
| Rs. 8,00,001 to Rs. 11,00,000 | 20% |
| Rs. 11,00,001 to Rs.20,00,000 | 30% |
| Above Rs. 20,00,000 | 36% |
Source: Inland Revenue Department. income-tax-rate-in-nepal-2079-80
6. Social Security Fund (SSF)
The Social Security Fund (SSF) is governed by the Social Security Act,2075. The Act requires every company/employer to enlist their name and its employees in the Social security fund.
The employees are entitled to Provident fund and gratuity from the first day of employment. The registration should be done at the Office of Social Security Fund.
Documents required for the registration of SSF for employer are:
- Company Registration Certificate
- PAN/VAT Certificate
- Details of Employer
- Application
Documents required for the registration of SSF for employee are:
- Employee Details
- Employee citizenship/National ID Card/PAN certificate/Passport
- Passport size photo of employee
The Company is required to make monthly contribution including Provident Fund and Gratuity to SSF in the following rate:
| Contribution | Provident Fund | Gratuity | Additional | Total |
| Employee | 10% | 1% | 11% | |
| Employer | 10% | 8.33% | 1.67% | 20% |
The employee shall deposit 11% and the employer shall add 20% of the basic salary per month (31% of the basic salary of the employee) to the Fund every month.
7. Leave and Holidays
The Labor Act, 2074, (section 40 – 48) has provided for the following list of holidays and leaves to the employees:
- Weekly leave: 1 day every week.
- Public leave (Public Holidays): 13 days including May Day, one additional day to female employees on International Women’s Day.
- Substitute Leave: Employees who has been engaged in work on a weekly or public leave are entitled to substitute leave within 21 days of the date of engagement in work.
- Annual Leave (Home Leave): 1 day for every 20 worked days.
- Sick Leave: Fully paid up to 12 days (previously half paid up to 15 days) – For those who have not completed one year of service, sick leave is provided on a proportional basis.
- Maternity Leave: Up to 14 weeks (fully paid for 60 days) including prenatal and postnatal periods. The leave must be taken at least 2 weeks prior and 6 weeks after the delivery. The female employee who has still birth or suffers miscarriage after 7 months or longer pregnancy is entitled to the leave.
- Paternity Leave: Up to 15 day fully paid.
- Mourning Leave: 13 days.
8. Termination
An employment contract can be terminated on various grounds as prescribed by the Labor Act, 2075. The company is restricted from terminating employment on any ground which has not been provided by the Labor Act.
A prior notice of Termination shall be given to the employee. Grounds for the termination of employment as per Labor Act is given below:
- Voluntary Termination
When an employee submits a resignation in written form to the employer, it is considered Voluntary Termination of employment. The employer shall accept the resignation within 15 days and provide a notice thereof to the employee. - Performance-based termination
If the employment performance is unsatisfactory or below standard in 3 consecutive performance appraisals then the employment may be terminated by the company. Before terminating the employment, the Company is required to give 7 days time to the concerned employee to present his/her explanation. - Compulsory Retirement
The employment contract is terminated after the employee attains the legal age of retirement, i.e. 58 years. - Medical grounds
Employment contract may be terminated due to health reasons as well. It is terminated on the recommendation of a doctor, if the employee is physically or mentally disabled or injured, rendering him/her unable to work, or requiring him/her a long period of treatment which affects the work of the entity. The employment of a worker undergoing the treatment cannot be terminated until 6 months unless it is certified by a medical practitioner that he/she won’t be able to return to work.