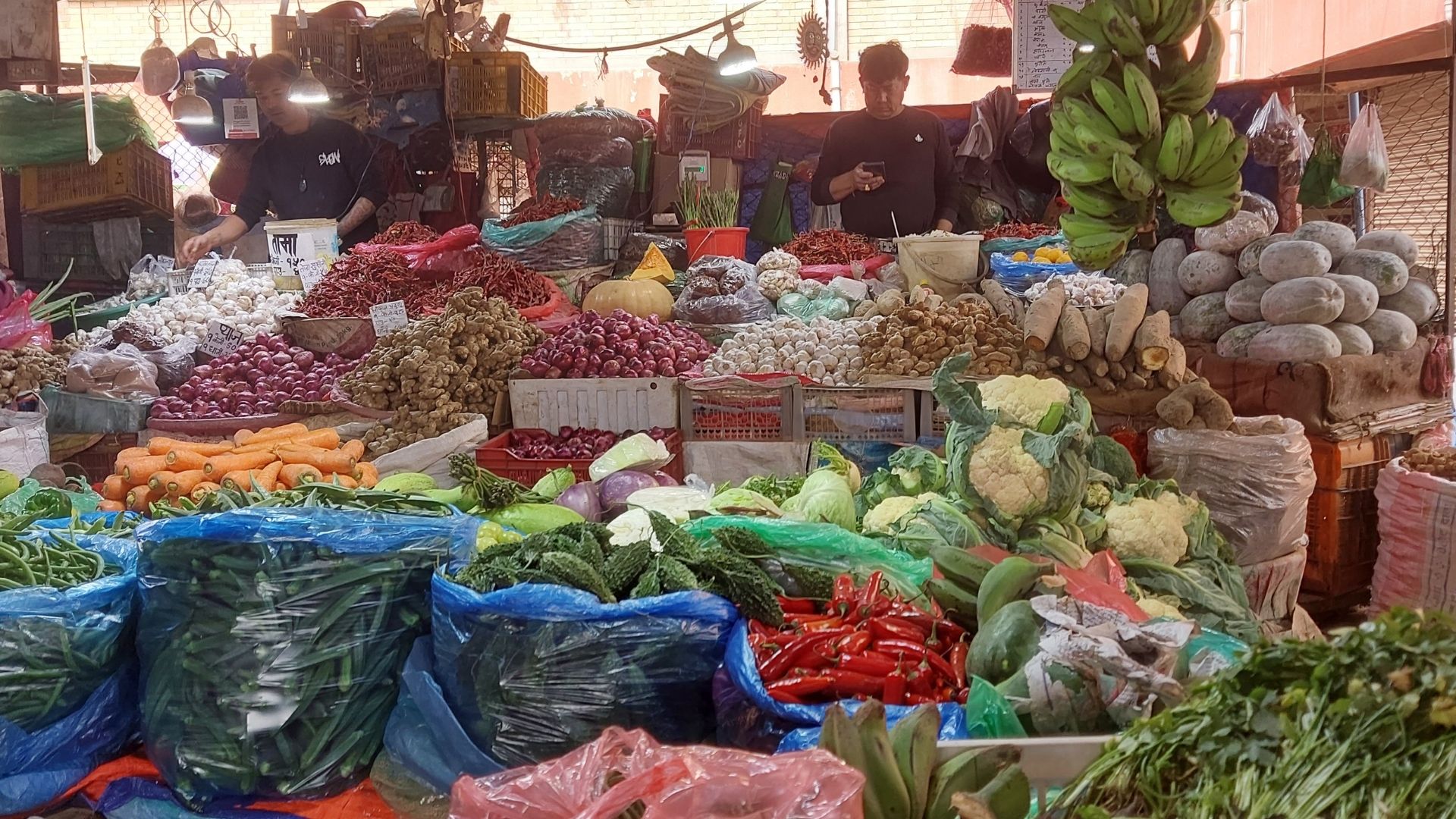
This course helps small and medium enterprises in Nepal implement effective inventory management systems to:
- Reduce waste and overstocking
- Prevent stockouts and missed sales
- Improve cash flow and decision-making
1. Understanding Inventory
1.1 What is Inventory?
Inventory refers to the goods and materials a business holds for the purpose of resale or production.
1.2 Types of Inventory
- Raw Materials – Inputs for production (e.g., fabric, spices)
- Work-in-Progress (WIP) – Items partially completed
- Finished Goods – Ready-to-sell products
- MRO Supplies – Maintenance, Repair, and Operating Supplies (e.g., tools, packaging)
1.3 Why Inventory Management is Important
- Frees up capital tied in unsold goods
- Reduces waste and theft
- Helps meet customer demand consistently
- Essential for VAT, PAN, and audit compliance in Nepal
2. Common Inventory Challenges for Nepal-Based MSMEs
- Overstocking due to inaccurate demand estimation
- Tracking stock manually or from memory
- Spoilage or theft in storage
- Seasonal demand fluctuations
- Lack of organized storage
- No integration between inventory and sales records
3. Inventory Management Methods
3.1 First In, First Out (FIFO)
Sell older stock first to avoid spoilage or obsolescence.
3.2 Economic Order Quantity (EOQ)
A formula to determine the ideal order quantity that minimizes inventory costs.
3.3 ABC Analysis
- A items: High value, low quantity
- B items: Moderate value and quantity
- C items: Low value, high quantity
3.4 Reorder Point System
Set minimum stock levels that automatically trigger reordering.
Example: If sanitizer stock falls below 10 units, reorder 50 units.
4. Setting Up an Inventory System
4.1 Manual System
Use notebooks or registers. Include:
- Date
- Product
- Stock In
- Stock Out
- Balance
- Remarks
4.2 Spreadsheet-Based System
Use Excel or Google Sheets with columns for:
- Product Code
- Product Name
- Opening Balance
- Purchases
- Sales
- Closing Balance
- Location or Shelf
4.3 Digital Tools for Nepali MSMEs
- Tigg – Accounting and inventory
- Khatapana – Stock and ledger in Nepali
- SmartBiz – POS and inventory management
- Google Sheets – Free and customizable
5. Stock Counting and Audits
5.1 Recommended Frequency
- Daily: High-turnover items
- Weekly: Perishables
- Monthly/Quarterly: Non-perishable bulk stock
5.2 Tips for Effective Stock Counting
- Count during non-peak hours
- Use printed or digital checklists
- Assign stock checks to trusted staff
- Compare physical count with records
6. Integrating Inventory with Sales and Purchases
- Record all purchases and sales promptly
- Connect stock records to POS or billing systems
- Analyze sales trends to forecast future needs
- Monitor for shrinkage and losses
7. Storage and Inventory Safety
- Clearly label all stock (product name, batch, expiry)
- Use shelves or pallets to avoid ground contact
- Ensure good lighting, airflow, and pest control
- Keep high-value items locked or restricted
- Separate damaged or returned items from saleable stock
8. Seasonal and Demand-Based Planning
- Anticipate peak seasons: Dashain, Tihar, tourist season, school year
- Review past sales data to predict future demand
- Avoid over-ordering before low-demand periods
9. Key Inventory Metrics to Track
| Metric | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Stock Turnover | How often stock is sold and replenished |
| Holding Cost | Cost of storing unsold inventory |
| Dead Stock | Items that haven’t sold in a long time |
| Shrinkage | Inventory loss from damage or theft |
10. Sector-Specific Inventory Tips
Retail
- Group items by category (e.g., electronics, clothing)
- Use basic barcode systems if possible
- Bundle slow-moving with popular items to improve clearance
Manufacturing
- Track raw materials and finished goods separately
- Monitor work-in-progress inventory
- Maintain minimum buffer stock to avoid production halts
Final Tips
- Begin with simple tools—even a notebook is better than no system
- Review inventory weekly or monthly
- Train staff on how to record stock properly
- Track best- and worst-performing items regularly
- Use stock data to make smarter purchasing and marketing decisions