Understanding Sales for MSMEs
1.1 What is Sales?
- The process of helping a customer solve a problem in exchange for value.
- Not just selling products—it’s about building relationships.
1.2 Why Sales is Critical for MSMEs
- Directly impacts cash flow.
- Sales equals sustainability.
- Competitive advantage in a saturated or price-sensitive market.
Knowing Your Product & Market
2.1 Understand What You’re Selling
- Product/service features
- Benefits to customers
- Unique Selling Proposition (USP)
2.2 Know Your Customer (Nepal Context)
- Local vs tourist markets
- Urban vs rural preferences
- B2B (business to business) vs B2C (business to consumer)
2.3 Competitor Analysis
- Who are your main competitors?
- What are their pricing, packaging, service levels?
Basic Sales Techniques
3.1 The AIDA Sales Funnel
- Attention: How will you attract customers?
- Interest: How will you maintain their attention?
- Desire: How will you make them want your product?
- Action: How do you close the sale?
3.2 Active Listening & Problem Solving
- Let the customer speak first.
- Understand the need before pitching.
3.3 Building Trust (especially in rural Nepali communities)
- Deliver what you promise.
- Be consistent in pricing and quality.
- Offer after-sales service (when applicable).
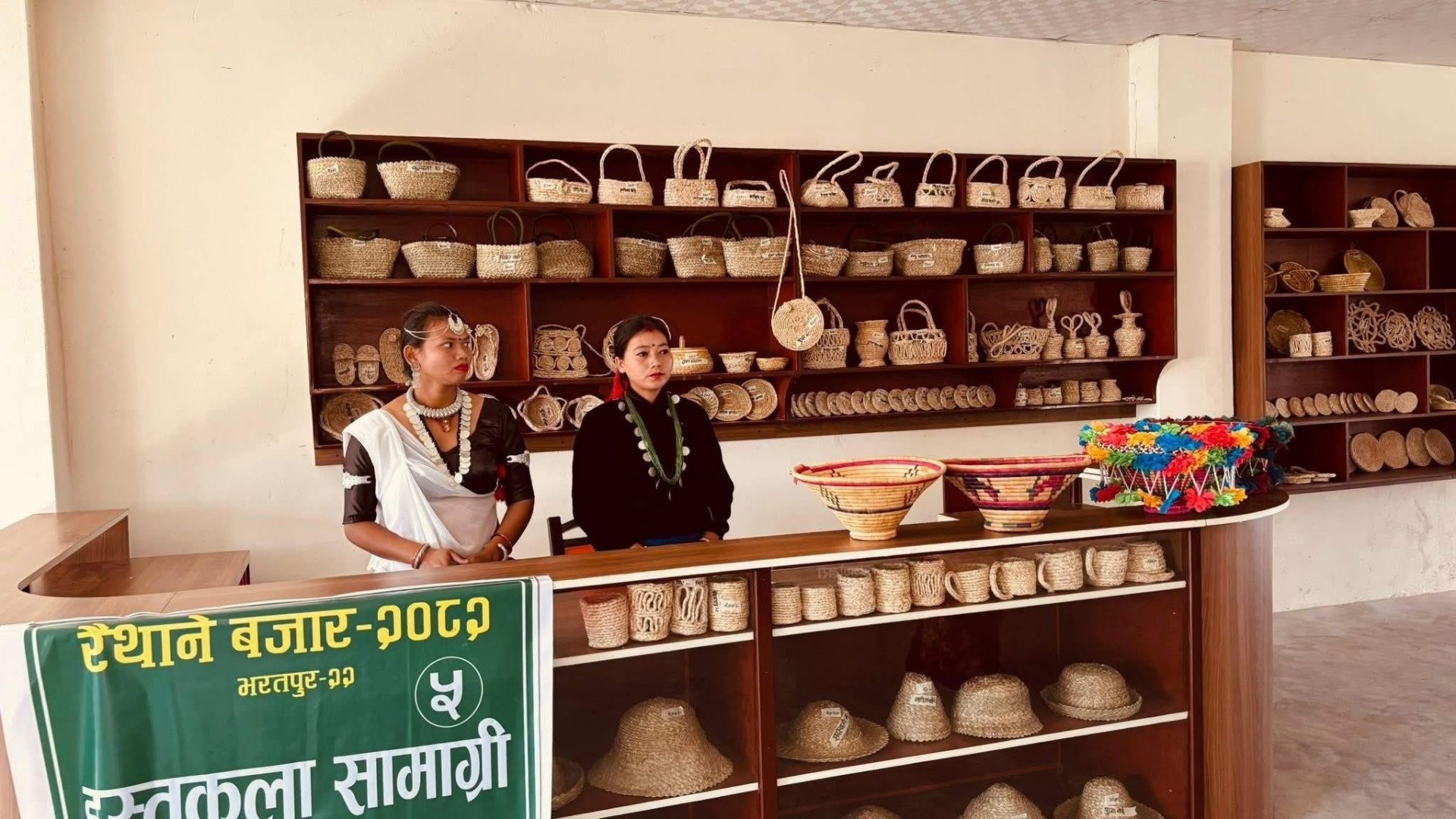
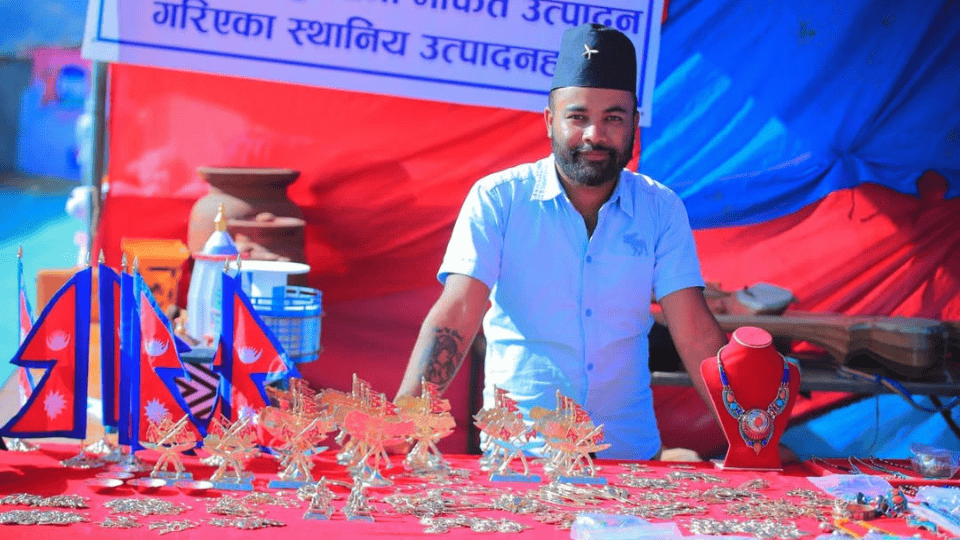
Sales Channels for Nepalese MSMEs
4.1 Offline Sales Channels
- Retail shopfront
- Local haat bazaars (weekly markets)
- Exhibitions and trade fairs
4.2 Online Sales Channels
- Facebook/Instagram for Business (popular in Nepal)
- HamroBazar, SastoDeal, Daraz
- Viber & WhatsApp groups
4.3 Partnering with Distributors and Wholesalers
- Identify trustworthy distributors
- Negotiate favorable margins
Pricing and Negotiation
5.1 Pricing Strategy
- Cost-based pricing (Cost + Profit)
- Market-based pricing
- Perceived value pricing
5.2 Handling Negotiation
- Be respectful but firm
- Offer value-adds instead of discounts
- Know your walk-away price
Record Keeping and Sales Tracking
6.1 Daily Sales Log (Simple Format)
- Date, product sold, quantity, price, customer name (if known), payment status
6.2 Analyze Sales Patterns
- What days/months are best?
- Which products sell most?
- Who are your regular customers?
6.3 Use of Free Tools
- Google Sheets or Excel
- Tally (basic version)
- Local accounting apps (e.g., Tigg, Khatapana, SmartBiz)
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
7.1 Keep Customer Contacts
- Phone, location, what they bought
- Follow-up for feedback or repeat purchase
7.2 Loyalty Programs
- Discount on 5th purchase
- Refer-a-friend program
Sales Tips for Specific Sectors
8.1 Tourism-Related MSMEs
- Sell experiences, not just products
- Focus on TripAdvisor/Google reviews
8.2 Agricultural MSMEs
- Build bulk buying relationships
- Target co-ops or government programs
8.3 Manufacturing MSMEs
- Sell to wholesalers and retailers
- Build product catalog or samples
Sales Pitching Practice (Roleplay)
9.1 Create a Pitch Script
- 30-second intro
- Benefits
- Call-to-action
9.2 Practice with Peers or Staff
- Use real scenarios
- Get feedback
Overcoming Common Sales Challenges in Nepal
Common Problems:
- Price-sensitive customers
- Credit buying culture
- Lack of foot traffic
Solutions:
- Focus on value, not just price
- Have clear credit policies
- Promote online to expand reach