The government’s latest fiscal budget places emphasis on promoting exports and enhancing the country’s competitiveness in global markets. From simplifying trade processes to incentivizing high-potential sectors like agriculture, IT, and herbal products, the budget outlines a range of strategic measures.
While the budget acknowledges the country’s persistent trade deficit is driven by insufficient export growth and diversification, coupled with weak domestic production capacity that has caused a surge in consumer goods imports. According to the new budget, the government will adopt product-specific exports strategies focused on value-added and competitive advantage.
Some of the initiatives featured in this year’s budget are highlighted below—
EXIM process simplified
Exporters and Importers are no longer provisioned to provide bank guarantee of NRs 3 lakh to get EXIM code. This enables small and new businesses to participate in international trade without committing a significant amount of capital as collateral.
Special concession to industries in SEZs and Industrial Zones
The government has introduced new budget measures aimed at boosting industrial capacity and export growth. New industries in Industrial Zones and Special Economic Zones (SEZs) will receive three year operational concessions. Export-oriented industries in Industrial Zones that export over 30% of their output will receive benefits equal to SEZs. The monthly rental rate has also been reduced from NRs 20 to NRs 5 per meter square to ease operational cost.
Boost agriculture and livestock exports
The government has announced plans to upgrade processing plants, quarantines and laboratories to meet international standards and obtain global certification for high-value agricultural products such as fruits, vegetables, meat, and others to boost their exports. This includes quality standards, certification, laboratory testing, and branding to promote the export of products such as large cardamom, tea, coffee, ginger, turmeric, cinnamon, Akbare chili, timur (Sichuan pepper), and incense materials.
The plan also includes promoting fresh meat exports by encouraging large-scale farming and improving quality. To boost productivity, the government aims to artificially inseminate 850,000 livestock under a breed improvement program and produce 55 million vaccine doses to control livestock diseases and prevent outbreaks. A budget of Rs 850 million has been allocated for these initiatives.
Additionally, It will complete major agro market constructions and start infrastructure development in Semalar, Rupandehi to support agricultural exports.
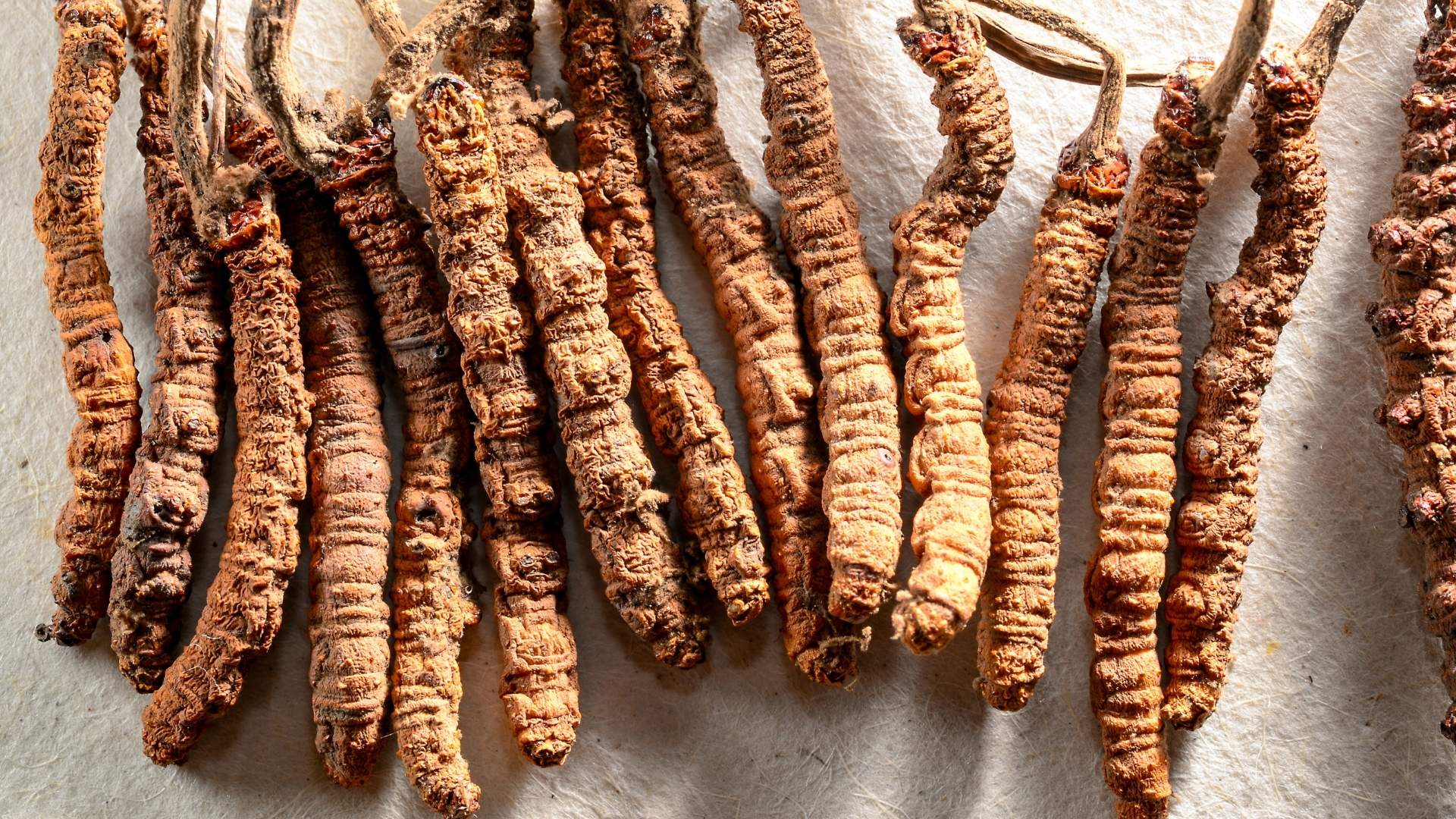
Incentivize Medicinal and Herbal products (MAPs)
With the aim to promote the production and trade of natural and herbal products, the government plans to actively engage the private sector to identify economically viable MAP products (Medicinal and Aromatic Plants) for collection, processing, and value addition. Based on feasibility study, selected plants will be supported through infrastructure and incentives to enable product development for both domestic and export markets. For this total budget of NRs 20 crore will be allocated.
Aid to jewelry exporters
The government will allow exporters to import gold and silver equivalent to their export volume, provided that more than 50% of their earnings are routed through formal channels. Moreover, jewelry exporters will be permitted to access bonded warehouse facilities, to reduce operational cost and logistical hurdles, and improve the export’s competitiveness.
Tapping potential of natural resources
The government plans to host an international mining conference to tap into Nepal’s mineral resources and promote them as export commodities. Alongside this, feasibility studies will guide the identification and development of economically viable herbal and forest-based products for both domestic use and export, with active private sector participation.
Tax relief for IT service export
The budget has announced 75% tax exemption on income tax for earnings generated from exporting IT services. Furthermore, individuals or companies providing IT services to foreign clients from within Nepal will be taxed only 5% income tax.
Outbound investment and profit repatriation
Nepali companies will be allowed to establish overseas sales branches and processing units for semi-processed goods. However, only up to 25% of their annual export income can be reinvested abroad, and at least 50% of the profits have to be repatriated. All these investments require prior approval from the Investment Board of Nepal.